Welding Position is the type or position of the connection to be welded, this welding position is based on the material or product to be welded. In welding technology, all of them have coding based on the type of connection. For fillet connections, it is symbolized with positions 1F, 2F, 3F, and 4F, while for groove or bevel connections it is symbolized by 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G.
Fillet weld is a method for combining two parts of metal vertically or slightly at an angle. They are also known as T connections or Lap connections (Lap connections are when pieces of metal overlap and the edges are welded). Welds are in the form of triangles and are commonly used when connecting pipes. This is also called closed welding because the weld metal does not need to be cut to join. Groove welds are made in metal grooves that will be joined. Need full penetration to have strong joints. This weld is used for the tip and butt joint connections. Groove welds are stronger than fillet welds. In general, basic welding positions consist of 4 types namely flat position, horizontal position, vertical position, and overhead position.
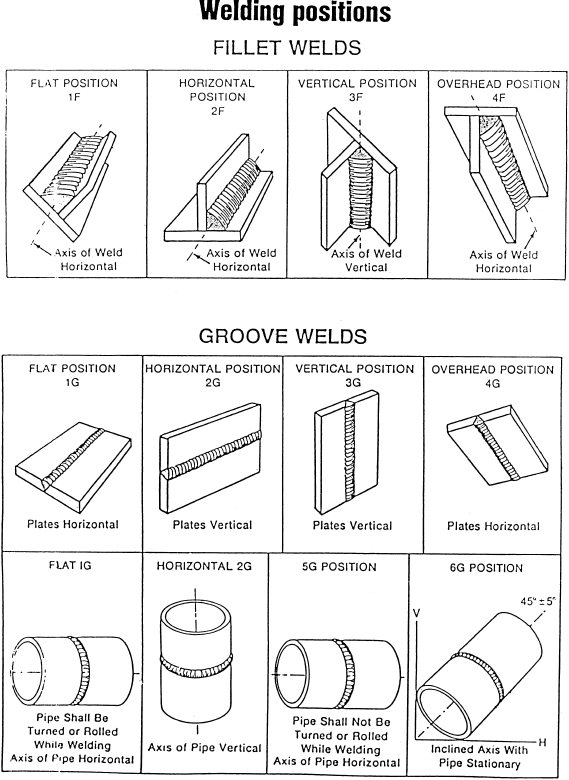
In the following, symbols are often used to explain the welding position:
The (4G) Groove Position is performed where groove weld is rotated so that the filler material goes in in overhead. This position is the hardest on plate material and will most of the time qualify you in the Flat position also.
Welding Position for Groove connection.
– 1G (Flat Welding Position).
– 2G (Horizontal Welding Position).
– 3G (Vertical Welding Position).
– 4G (Welding Position Overhead or Overhead).
Overhead Welding Position 4F and 4G. The number 4 position is overhead. It is important to to keep a very short arc when welding overhead. Pipe Welding Positions. There are four pipe welding position. If a position has the letter 'R' that means the pipe can be rolled while welding. The 4G position is a groove weld in the overhead position which qualifies a welder to weld in the flat, horizontal, and overhead positions with a single test. When combining the 3G and 4G welding certifications, the welder is qualified to do structural welding in all positions.
Welding position for Fillet connections.
– 1F (Flat Welding Position).
– 2F (Horizontal Welding Position).
– 3F (Vertical Welding Position).
– 4F (Welding Position Overhead or Overhead).
what are the 1G 2G 5G 6G pipe welding positions?
In the construction phase of a project in the oil and gas industry, we often find welding activities on pipes or welding on tanks. To maintain the quality of welding, professional organizations (ASME, AWS, ISO, JWES) make rules and classification of welding positions. All welder involved in construction needs to be certified according to these positions. In general, the pipe welding position is divided into 2 types, namely the welding position on the groove joint and the welding position on the fillet joint. Mostly welding connections on pipes use groove joints type so we often hear the term pipe welding position. The pipe welding position is divided into 4 groups, namely 1G, 2G, 5G and 6G.
Comparisons welding positions between ISO standard positions and ASME / AWS:
| No | Welding Position (ISO) | Welding Position (ASME / AWS) |
| 1 | PA | 1G / 1F |
| 2 | PB | 2F |
| 3 | PC | 2G |
| 4 | PD | 4F |
| 5 | PE | 4G |
| 6 | PF | 3G Uphill |
| 7 | PG | 3G Downhill |
| 8 | PH | 5G Uphill |
| 9 | PJ | 5G Downhill |
| 10 | H-L045 | 6G Uphill |
| 11 | J-L045 | 6G Downhill |
There are two aspects of welding; skill and knowledge. The skill of the welder is evaluated by welder performance qualification. This is an important demonstration of the welder's ability to deposit a quality weld. So, things like position, backing, uphill, and downhill, etc., are very important. According to ASME BPVC section IX, A welder shall be requalified whenever a change is made in one or more of the essential variables listed for each welding process.
1G pipe welding position
this is the easiest welding position. 1G welding position is a position where the pipe is in a horizontal position and the pipe can be rotated against the horizontal axis or the X-axis. The welder conducts welding from the top of the pipe. Welder position does not change.
2G pipe welding position
this is a welding position that is easy to do. 2G welding position is a position where the pipe is in a vertical direction and weld axis in horizontal direction. The welder conducts welding from the side of the pipe with horizontal welding direction.
5G pipe welding position
5G welding position is a position where the pipe is in a horizontal or X-axis position but the pipe is fixed or cannot be rotated. Welder conducts welding while moving around the pipe. This position is almost the same as the 1G position, only the pipe cannot be rotated. It is also named as PF in ISO/EN standards. In 5G, welding is done vertically either upwards or downwards.
6G pipe welding position
This pipe welding position is the most difficult welding position. Only the welder has enough experience capable of welding with a 6G position. Pipe in a sloping position which is around 45 degrees from the horizontal axis (X-axis) or 45 degrees from the vertical axis (Y-axis). The pipe cannot be rotated so the welder must do welding while moving around the pipe.
Welding position is an important variable to determine weld quality. If a welder has the qualification of 1G position, he is not permitted to conduct welding in more difficult positions such as 6G position. But on the contrary, if the welder has a 6G position qualification, then he is permitted to carry out welding in the 1G position. A welding inspector is responsible to verify this requirement to be implemented.
3g And 4g Welding Certification
1G, 2G, 5G, 6G Welding Positions limitation in WPS
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section IX also makes very good guidelines and limitations about welding positions in WPS for the specific welding process. Take an example for GTAW process ( for other welding processes, we do the same thing, check each variable to know what happen on it when we change them ). For the GTAW process, any addition of a welding position is categorized as an essential variable. This means the welding position has an important effect on weld quality results. QW-405.1 states a change in the position qualified is essential.
related article:
- welding procedure specification or (WPS)
- GTAW welding process

Welding Positions are the positional relation between the welder and the production piece to be welded. In ISO 15614-1, ASME IX and AWS D1.1 (referring to AWS A3.0), the ideals are pretty similar, but have a different naming system.
Mig Welding 4g Position
If you'd like to read some more on other issues, you can use our blog, or follow us on facebook, twitter and linkedin,
Below this is a diagram which you can use to define the horizontal positions (this means the weld progression is done horizontally). This whole article and the diagrams below will already be featuring the conversion between ISO standards to AWS / ASME standards naming system.
You'll notice that you'll essentially only need to pay attention to half of this diagram, as the other half is exactly the same (mirrored), which means the PC / 2G position is the same on either side of the plate or pipe.
Horizontal travel positions
PA / 1G / 1F: This is the flat position, in which the welder has the piece right below the torch, this is used for butt or groove welds, although it can be used for fillet welds.
PB / 2F: This is the horizontal position for fillet welds. The welder will be holding the torch at around 45º most of the times (although it depends on the plate or pipe position) with the piece right next to him:
PC / 2G: Commonly referred to as the horizontal position for butt welds. The piece will be directly parallel to the welders body and he'll usually weld the piece while it is right in front of him:
PD / 4F: This is the overhead position for fillet welds. The welder will be holding the torch at around 45º most of the times (even if it depends on the plate or pipe position), this time while being below the piece.
PE / 4G: Overhead position for butt welds. The welder will be holding the torch from directly below the piece. It is quite hard as a position and requires proper weld parameter settings.
Uphill and Downhill travel positions
Okay so the previous part of this post with the respective diagram is essentially referring to the horizontal travel welding positions, in which the weld progression is perpendicular to the welder's position. We shall now discuss the positions in which weld progression is parallel to the welder's position.
PF / 3G Uphill: Vertical up for butt or fillet welds. The welder uses the metal from the lower parts of the test piece and some superficial tension to perform welding against the force of gravity, while aiming the torch at around 45º.
PG / 3G Downhill: Vertical down for butt or fillet welds. The welder will use the metal from the upper parts of the test piece and the electric arc's own kinetic force (as well as some superficial tension) to maintain the weld puddle. This is a good position in terms of productivity, and there are already very competent systems to weld in this position on semi-automatic welding.
PH / 5G Uphill: Vertical up position for pipe butt welds. This is a very common way of welding pipes manually. The welder will be welding in three different positions, starting with the overhead position, then going through the horizontal position, and finishing on the flat position
In the following, symbols are often used to explain the welding position:
The (4G) Groove Position is performed where groove weld is rotated so that the filler material goes in in overhead. This position is the hardest on plate material and will most of the time qualify you in the Flat position also.
Welding Position for Groove connection.
– 1G (Flat Welding Position).
– 2G (Horizontal Welding Position).
– 3G (Vertical Welding Position).
– 4G (Welding Position Overhead or Overhead).
Overhead Welding Position 4F and 4G. The number 4 position is overhead. It is important to to keep a very short arc when welding overhead. Pipe Welding Positions. There are four pipe welding position. If a position has the letter 'R' that means the pipe can be rolled while welding. The 4G position is a groove weld in the overhead position which qualifies a welder to weld in the flat, horizontal, and overhead positions with a single test. When combining the 3G and 4G welding certifications, the welder is qualified to do structural welding in all positions.
Welding position for Fillet connections.
– 1F (Flat Welding Position).
– 2F (Horizontal Welding Position).
– 3F (Vertical Welding Position).
– 4F (Welding Position Overhead or Overhead).
what are the 1G 2G 5G 6G pipe welding positions?
In the construction phase of a project in the oil and gas industry, we often find welding activities on pipes or welding on tanks. To maintain the quality of welding, professional organizations (ASME, AWS, ISO, JWES) make rules and classification of welding positions. All welder involved in construction needs to be certified according to these positions. In general, the pipe welding position is divided into 2 types, namely the welding position on the groove joint and the welding position on the fillet joint. Mostly welding connections on pipes use groove joints type so we often hear the term pipe welding position. The pipe welding position is divided into 4 groups, namely 1G, 2G, 5G and 6G.
Comparisons welding positions between ISO standard positions and ASME / AWS:
| No | Welding Position (ISO) | Welding Position (ASME / AWS) |
| 1 | PA | 1G / 1F |
| 2 | PB | 2F |
| 3 | PC | 2G |
| 4 | PD | 4F |
| 5 | PE | 4G |
| 6 | PF | 3G Uphill |
| 7 | PG | 3G Downhill |
| 8 | PH | 5G Uphill |
| 9 | PJ | 5G Downhill |
| 10 | H-L045 | 6G Uphill |
| 11 | J-L045 | 6G Downhill |
There are two aspects of welding; skill and knowledge. The skill of the welder is evaluated by welder performance qualification. This is an important demonstration of the welder's ability to deposit a quality weld. So, things like position, backing, uphill, and downhill, etc., are very important. According to ASME BPVC section IX, A welder shall be requalified whenever a change is made in one or more of the essential variables listed for each welding process.
1G pipe welding position
this is the easiest welding position. 1G welding position is a position where the pipe is in a horizontal position and the pipe can be rotated against the horizontal axis or the X-axis. The welder conducts welding from the top of the pipe. Welder position does not change.
2G pipe welding position
this is a welding position that is easy to do. 2G welding position is a position where the pipe is in a vertical direction and weld axis in horizontal direction. The welder conducts welding from the side of the pipe with horizontal welding direction.
5G pipe welding position
5G welding position is a position where the pipe is in a horizontal or X-axis position but the pipe is fixed or cannot be rotated. Welder conducts welding while moving around the pipe. This position is almost the same as the 1G position, only the pipe cannot be rotated. It is also named as PF in ISO/EN standards. In 5G, welding is done vertically either upwards or downwards.
6G pipe welding position
This pipe welding position is the most difficult welding position. Only the welder has enough experience capable of welding with a 6G position. Pipe in a sloping position which is around 45 degrees from the horizontal axis (X-axis) or 45 degrees from the vertical axis (Y-axis). The pipe cannot be rotated so the welder must do welding while moving around the pipe.
Welding position is an important variable to determine weld quality. If a welder has the qualification of 1G position, he is not permitted to conduct welding in more difficult positions such as 6G position. But on the contrary, if the welder has a 6G position qualification, then he is permitted to carry out welding in the 1G position. A welding inspector is responsible to verify this requirement to be implemented.
3g And 4g Welding Certification
1G, 2G, 5G, 6G Welding Positions limitation in WPS
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section IX also makes very good guidelines and limitations about welding positions in WPS for the specific welding process. Take an example for GTAW process ( for other welding processes, we do the same thing, check each variable to know what happen on it when we change them ). For the GTAW process, any addition of a welding position is categorized as an essential variable. This means the welding position has an important effect on weld quality results. QW-405.1 states a change in the position qualified is essential.
related article:
- welding procedure specification or (WPS)
- GTAW welding process
Welding Positions are the positional relation between the welder and the production piece to be welded. In ISO 15614-1, ASME IX and AWS D1.1 (referring to AWS A3.0), the ideals are pretty similar, but have a different naming system.
Mig Welding 4g Position
If you'd like to read some more on other issues, you can use our blog, or follow us on facebook, twitter and linkedin,
Below this is a diagram which you can use to define the horizontal positions (this means the weld progression is done horizontally). This whole article and the diagrams below will already be featuring the conversion between ISO standards to AWS / ASME standards naming system.
You'll notice that you'll essentially only need to pay attention to half of this diagram, as the other half is exactly the same (mirrored), which means the PC / 2G position is the same on either side of the plate or pipe.
Horizontal travel positions
PA / 1G / 1F: This is the flat position, in which the welder has the piece right below the torch, this is used for butt or groove welds, although it can be used for fillet welds.
PB / 2F: This is the horizontal position for fillet welds. The welder will be holding the torch at around 45º most of the times (although it depends on the plate or pipe position) with the piece right next to him:
PC / 2G: Commonly referred to as the horizontal position for butt welds. The piece will be directly parallel to the welders body and he'll usually weld the piece while it is right in front of him:
PD / 4F: This is the overhead position for fillet welds. The welder will be holding the torch at around 45º most of the times (even if it depends on the plate or pipe position), this time while being below the piece.
PE / 4G: Overhead position for butt welds. The welder will be holding the torch from directly below the piece. It is quite hard as a position and requires proper weld parameter settings.
Uphill and Downhill travel positions
Okay so the previous part of this post with the respective diagram is essentially referring to the horizontal travel welding positions, in which the weld progression is perpendicular to the welder's position. We shall now discuss the positions in which weld progression is parallel to the welder's position.
PF / 3G Uphill: Vertical up for butt or fillet welds. The welder uses the metal from the lower parts of the test piece and some superficial tension to perform welding against the force of gravity, while aiming the torch at around 45º.
PG / 3G Downhill: Vertical down for butt or fillet welds. The welder will use the metal from the upper parts of the test piece and the electric arc's own kinetic force (as well as some superficial tension) to maintain the weld puddle. This is a good position in terms of productivity, and there are already very competent systems to weld in this position on semi-automatic welding.
PH / 5G Uphill: Vertical up position for pipe butt welds. This is a very common way of welding pipes manually. The welder will be welding in three different positions, starting with the overhead position, then going through the horizontal position, and finishing on the flat position
PH / 5G Downhill: Vertical down position for pipe butt welds. This is a very productive way of welding pipes manually, but should be done only with specific equipment for pipe welding against the force of gravity. The welder will be welding in three different positions, starting with the flat position, then going through the horizontal position, and finishing on the overhead position.
H-L045 / 6G Uphill and J-L045 / 6G Downhill: The hardest positions for a welder to perform. Usually only performed on weld tests, in order to qualify a welder for all other positions. This is essentially the same as PH / PJ / 5G but with the pipe at a 45º angle.
J-L045 / 6G Downhill
So, to summarize, these are the comparisons between ISO standard positions and ASME / AWS nomenclature:
Hotspot shield. Welding Position (ISO) | Welding Position (ASME / AWS) |
| PA | 1G / 1F |
PB | 2F |
PC | 2G |
| PD | 4F |
PE | 4G |
PF | 3G Uphill |
PG | 3G Downhill |
5G Uphill | |
PJ | 5G Downhill |
H-L045 | 6G Uphill |
| J-L045 | 6G Downhill |
I hope this has been helpful, if you'd like to read more, you may follow us on facebook, twitter and linkedin.
You may also check our other blog posts here.
Best regards,
Tiago Pereira
CEO at WeldNote, Welding Management Software
